Go-Kit 介绍
Go Kit 并不是一个框架而是一个包的集合。它可以帮助我们构建健壮、可靠、可维护的微服务,这点在生产环境中已得到验证。所以对于想要实现一个简洁架构的 Go 开发者来说,了解 Go Kit 包是非常必要的。
关键概念
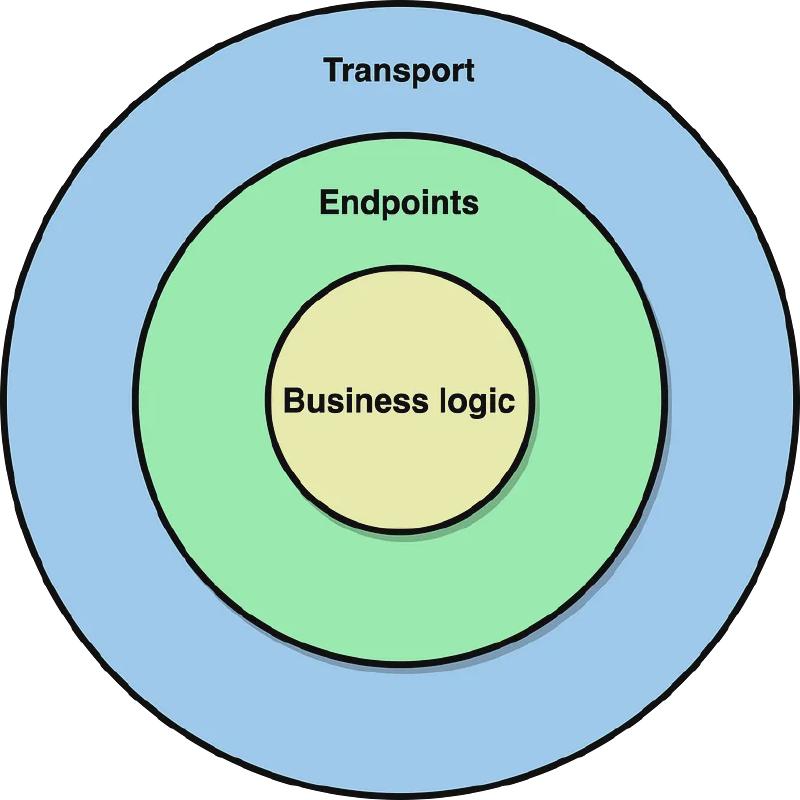
Go Kit 构建的服务可以分为三层:
- Transport (传输层)
- Endpoint (端点层)
- Service (服务层)
Transport
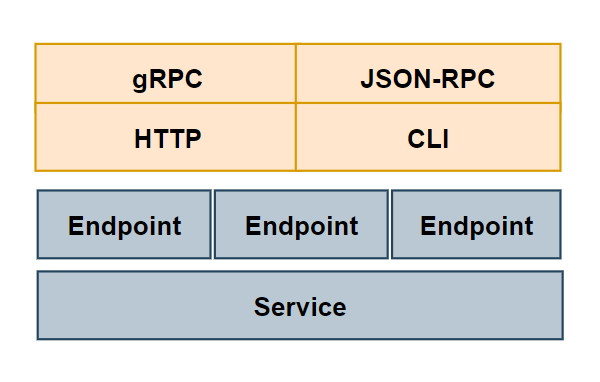
通信协议:提供多种传输协议的支持,包括 HTTP、gRPC、JSON-RPC、CLI 等。
数据编码:负责将数据在服务之间进行编码和解码。不同的通信协议需要不同的编解码方式。
Endpoint
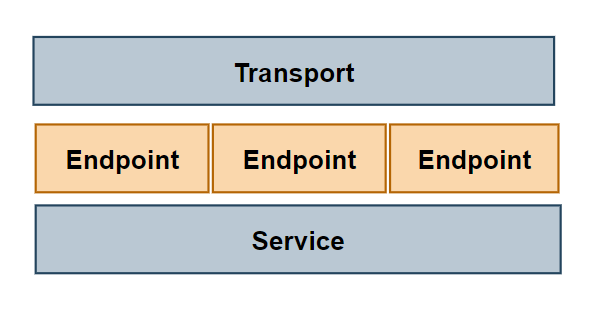
端点:是 Service 层的入口,对 Service 进行 wrapper。它是定义输入和输出定义用例的地方,用简洁架构术语来说,就是处理请求->调用 Service->返回响应。
请注意,端点是一个接收请求并返回响应的函数,它们都是 interface{},即 RequestModel 和 ResponseModel。理论上它也可以用类型参数(泛型)来实现。
config
中间件:通过一组中间件来组合和包装端点,实现例如日志记录、认证、限流等功能
Service
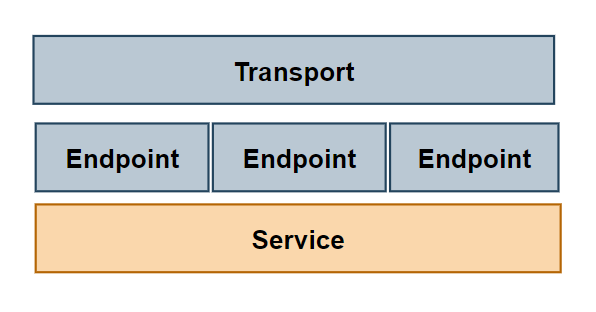
Service 层是实现所有业务逻辑的地方。服务不了解端点,端点和服务都不了解传输域。
Service 有多个 Endpoint 组成,每个 Endpoint 代表了一个具体功能。
简单示例
我们通过一个简单的微服务示例来加深对 Go-Kit 的理解。
假设我们要完成一个打招呼的功能,具体源码可以看 Go-Kit http 微服务示例。
文件结构如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| |-sample
|-endpoint/
|-endpoint.go
|-service/
|-service.go
|-transport/
|-transport.go
|-go.mod
|-main.go
|
- endpoint: 端口层
- service: 业务逻辑层
- transport: 传输层
服务层
服务层的代码非常简单:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package service
type IServer interface {
Hello(name string) string
Bye(name string) string
}
type Server struct {
}
func (s Server) Hello(name string) string {
return "Hello " + name
}
func (s Server) Bye(name string) string {
return "Bye " + name
}
|
如 Go Kit 所建议的,第一步是为我们的服务创建一个接口,接口有 2 个方法 Hello() 和 Bye() 。Server 结构体实现了这个接口。
另外,从这里我们可以看出,一个服务是可以有多个端点的,端点的代码稍后展示。
端点层
服务层定义了 Hello() 和 Bye() 两个方法,如果要调用这两个方法,我们需要创建两个端点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| package endpoint
import (
"context"
"sample/service"
"github.com/go-kit/kit/endpoint"
)
// Package
// Imports
// Types
// Constants AND Var
// Type Methods
// type Endpoint func(ctx context.Context, request interface{}) (interface{}, error)
type HelloRequest struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
}
type HelloResponse struct {
Msg string `json:"msg"`
}
type ByeRequest struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
}
type ByeResponse struct {
Msg string `json:"msg"`
}
func MakeHelloEndpoint(s service.IServer) endpoint.Endpoint {
return func(ctx context.Context, request interface{}) (interface{}, error) {
req := request.(HelloRequest)
msg := s.Hello(req.Name)
return HelloResponse{Msg: msg}, nil
}
}
func MakeByeEndpoint(s service.IServer) endpoint.Endpoint {
return func(ctx context.Context, request interface{}) (interface{}, error) {
req := request.(ByeRequest)
msg := s.Bye(req.Name)
return ByeResponse{Msg: msg}, nil
}
}
|
endpoint.go 文件中,我们分别定义了 Hello 和 Bye 的请求体和返回响应体。
同时我们也定义了 MakeHelloEndpoint() 和 MakeByeEndpoint() 两个函数,目的是将传输层的请求体转为服务层能够识别的结构体,并返回响应。
端点层对传输层一无所知,无论是哪种传输协议,都没有区别。
endpoint.Endpoint 定义如下:
1
| type Endpoint func(ctx context.Context, request interface{}) (response interface{}, err error)
|
传输层
在这一层中,我们可以有多种实现,如 HTTP, gRPC, AMPQ 等。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| package transport
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"net/http"
"sample/endpoint"
)
func HelloRequestDecoder(_ context.Context, r *http.Request) (interface{}, error) {
var request endpoint.HelloRequest
err := json.NewDecoder(r.Body).Decode(&request)
return request, err
}
func HelloResponseEncoder(_ context.Context, w http.ResponseWriter, response interface{}) error {
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
return json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(response)
}
func ByeRequestDecoder(_ context.Context, r *http.Request) (interface{}, error) {
var request endpoint.ByeRequest
err := json.NewDecoder(r.Body).Decode(&request)
return request, err
}
func ByeResponseEncoder(_ context.Context, w http.ResponseWriter, response interface{}) error {
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
return json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(response)
}
|
transport.go 文件分别定义了 Hello 和 Bye 的请求和响应的编解码函数。
目的是将传输层中的数据解析到端点层的结构体,将从端点层返回的结构体解析到传输层。
main
main.go 文件中,我们将使用所有层:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"sample/endpoint"
"sample/service"
"sample/transport"
"time"
httpTransport "github.com/go-kit/kit/transport/http"
)
func main() {
s := service.Server{}
// 调用端点层
hello := endpoint.MakeHelloEndpoint(s)
bye := endpoint.MakeByeEndpoint(s)
// 实例化 http 服务
helloServer := httpTransport.NewServer(
hello,
transport.HelloRequestDecoder,
transport.HelloResponseEncoder,
)
byeServer := httpTransport.NewServer(
bye,
transport.ByeRequestDecoder,
transport.ByeResponseEncoder,
)
// 开启 2 个协程监听端口 hello 和 bye 服务
go func() {
err := http.ListenAndServe(":8081", helloServer)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}()
go func() {
err := http.ListenAndServe(":8082", byeServer)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}()
for {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
fmt.Println(11111)
}
}
|
运行
1
2
3
4
| $ curl -s -XPOST -d'{"name": "Anna"}' localhost:8080/hello
{"msg":"Hello Anna"}
$ curl -s -XPOST -d'{"name": "Anna"}' localhost:8080/bye
{"msg":"Bye Anna"}
|
参考:Microservices in Go using the Go kit